Technology
MicroRNA
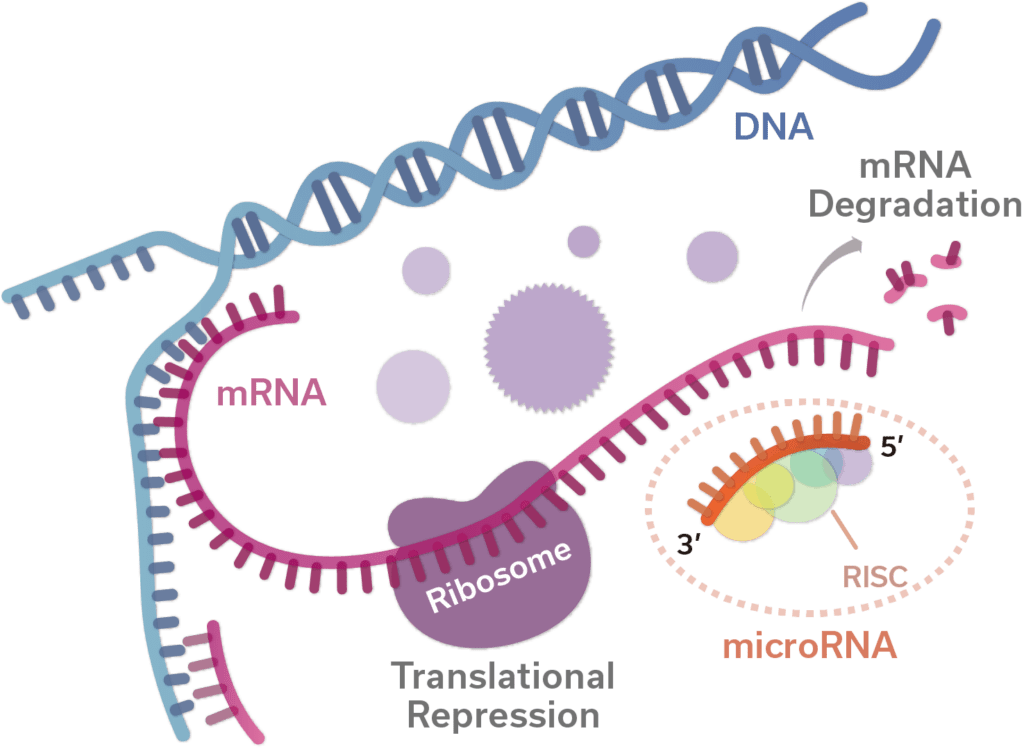
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding single strand RNAs, 18-22 nucleotides long, that function as crucial post-transcriptional regulators of intracellular metabolic processes via mRNA degradation or inhibition.
miRNA biomarkers for the (early) diagnosis of various diseases including cancer, are in the spotlight as Next-Gen Molecular Diagnostic Tools that address the unmet needs of molecular diagnostics. Numerous research projects are currently underway to commercialize these biomarkers.
Accurate detection and analysis of miRNA using conventional Real-Time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) techniques is challenging due to short sequence length and high sequence similarity between miRNAs.
Liquid Biopsy
Early Cancer Screening
The primary objective of early cancer screening is to assess asymptomatic individuals for the presence of cancer cells to screen for early cancer(stage 1~2) in order to increase the cancer survival rate.
For early cancer screening of asymptomatic individuals to be feasible, diagnostic tests have to be minimally invasive and inexpensive so that repeated testing is possible. Thus, blood or urine based liquid biopsies are the best option that meets all the aforementioned criteria.
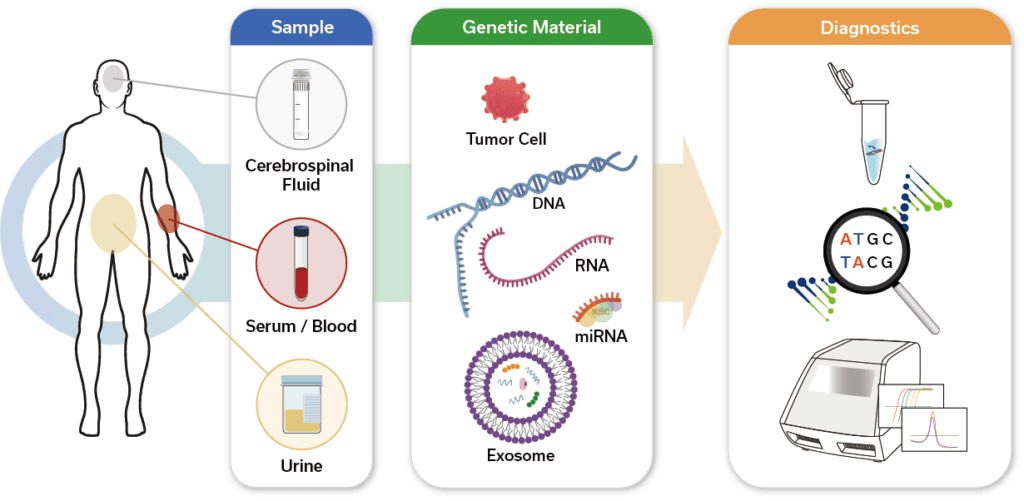
Liquid-Biopsy Using miRNA Biomarker
Liquid-Biopsy
Using miRNA Biomarker
Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) exist at low concentrations in the early stages of disease progression. Thus, early detection of diseases, including cancer, via liquid biopsy (blood, urine, etc.) of cfDNA is challenging. Alternatively, circulating miRNAs exist at high concentrations in liquid specimens despite being in the early stages of disease progression, thus enabling effective early detection.
Patient-Oriented Diagnostics
Liquid biopsy offers a non-invasive and cost-effective alternative to tissue biopsies.
An Effective Tool
for Early Cancer Diagnosis
Differential expression of miRNAs in cancer and other diseases facilitates its use as biomarkers.
miRNA-based diagnostics enable early detection and treatment thus improving patient outcomes and survival rates.

